
Alternatively, two perforated metal strips could be used.ģ) In case you have decided not to create a PCB, then take a piece of cardboard to support the LDRs. Drill one hole on each strip to attach the servo motors as shown. Alternatively, a cardboard piece could be used for the same.Ģ) Cut two metal strips out of light sheet metal. Here, heavy sheet metal is used as a base to support the entire structure. This is the logic behind the code used to create the solar tracker.ġ) To start the setup, create a base for the setup.
If the average of the two left LDRs is more, then the horizontal servo motor moves towards that side. If the average of the two right LDRs is more, then the horizontal servo motor rotates towards that side. The average of the two right and the two left LDRs is calculated. If the average of the two bottom LDRs is more, then the vertical servo motor rotates towards the bottom side. If the average of the two top LDRs is more, then the vertical servo motor rotates towards that side. The average of the two top and the two bottom LDRs is calculated. The bottom servo motor is the horizontal servo motor whereas the top servo motor is the vertical servo motor. To move the solar panel, we use servo motors. The values from these LDRs is read by the Arduino.
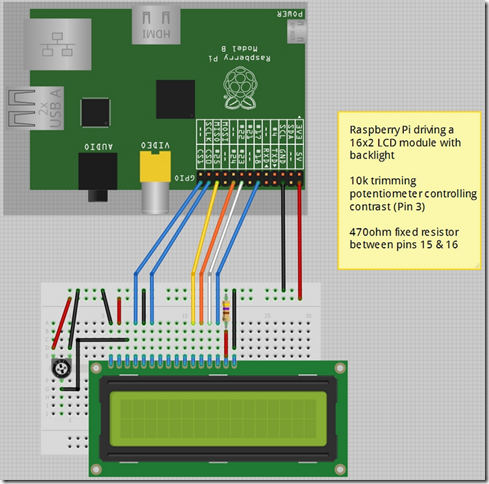
Here, the basic schematic was made using Fritzing.Ĥ Light dependent resistors are used on four corners of the solar panel to sense light.

The schematic can be made using either Fritzing or Eagle software. A solar tracker is a device which tracks the position of the sun and alters the position of the solar panel to maximize the power output of the system.Ħ) Raspberry Pi 3 Model B + keyboard, mouse, power supply and monitor for using RPiĬomponents required for manufacturing PCB (optional step). We can solve this problem by creating a solar tracker. One such problem is that the position of the sun throughout the day varies. However, the use of solar energy can face certain problems. Solar energy is the cleanest form of renewable energy which can be used to satisfy the growing need for energy while supporting sustainable development.

From transportation to agriculture, cooking to water heating, air conditioners to refrigerators, using laptops to watching television, using phones to watch silly videos to typing this very Instructable, everything needs energy! We will also learn how to create a graphic user interface using Processing.Īs we all know, energy is an indispensable part of our lives. This Instructable will teach you how to create a solar tracker using Arduino and Raspberry Pi 3 Model B.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
